Audit sampling
Audit sampling :
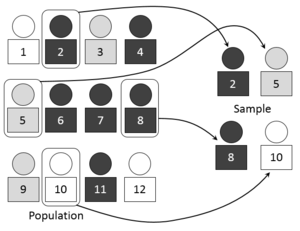
Audit sampling can be defined as the process of applying auditing procedure to under 100% of items in an organizations account balance in a every single unit might have an equal probability of being selected.
Sample methods:
1. Statistical sampling: It allows the measurement of sampling risk in planning the sample and evaluating the result.
2. Non statistical sampling: It does not quantify the sampling risk results are based on judgement.
Size of Sample:
Haphazard sampling: The haphazard sampling technique is the one adopted by the auditor in cases where the sample does not follow a structured technique. Haphazard sampling is, however, not appropriate during the use of statistical sampling.
2. Stratified sampling: This sampling technique involves the auditor to split items included in a sample into different section.
3. Systematic sampling : The systematic sampling is also referred as ‘interval’ sampling. This sampling technique involves the auditor to take the number of sampling units in the population and segregate this into the sample size so as to provide a sampling interval.
4. Block sampling : Block sampling is a sampling technique wherein the auditor applies measures to such items which occur in the same block of sequence or time. However, the block sampling technique should be used with caution as valid references cannot possibly be made beyond the examined period or block.
Audit sampling can be defined as the process of applying auditing procedure to under 100% of items in an organizations account balance in a every single unit might have an equal probability of being selected.
Sample methods:
1. Statistical sampling: It allows the measurement of sampling risk in planning the sample and evaluating the result.
2. Non statistical sampling: It does not quantify the sampling risk results are based on judgement.
Size of Sample:
Haphazard sampling: The haphazard sampling technique is the one adopted by the auditor in cases where the sample does not follow a structured technique. Haphazard sampling is, however, not appropriate during the use of statistical sampling.
2. Stratified sampling: This sampling technique involves the auditor to split items included in a sample into different section.
3. Systematic sampling : The systematic sampling is also referred as ‘interval’ sampling. This sampling technique involves the auditor to take the number of sampling units in the population and segregate this into the sample size so as to provide a sampling interval.
4. Block sampling : Block sampling is a sampling technique wherein the auditor applies measures to such items which occur in the same block of sequence or time. However, the block sampling technique should be used with caution as valid references cannot possibly be made beyond the examined period or block.